two tear testing for hpv|HPV Test vs. Pap Smear: What's the Difference? : distributor Primary Human Papillomavirus Testing In 2020, the American Cancer Society (ACS) updated its cervical cancer screening guidelines to recommend primary . See more webPara acessar os resultados dos exames, digite o Número do protocolo e clique em Consultar. Caso ocorra algum problema na visualização de laudos e imagens ou seja .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB5 de mai. de 2023 · 54K likes, 603 comments - sarah.estanislau on May 5, 2023: ":)"
There are now three recommended options for cervical cancer screening in individuals aged 30–65 years: primary hrHPV testing every 5 years, cervical cytology . See morePrimary Human Papillomavirus Testing In 2020, the American Cancer Society (ACS) updated its cervical cancer screening guidelines to recommend primary . See moreAlthough cervical cancer screening options have expanded, cervical cytology, primary hrHPV testing, and co-testing are all effective in detecting cervical . See more
Repeat human papillomavirus (HPV) testing or cotesting at 1 year is recommended for patients with minor screening abnormalities indicating HPV infection with low risk of underlying CIN 3+ . The test can be done by itself (primary HPV test) or at the same time as a Pap test (called a co-test). You won’t notice a difference in your exam if you have both tests done. The . The new ACS guidelines recommend that individuals with a cervix at average risk for cervical cancer begin screening at age 25 with a primary HPV test alone every five years. This applies to most women. Milbourne notes that .
What to expect when getting an HPV test or a pap smear. HPV tests and pap smears help reduce cervical cancer risk by detecting abnormal cervical cells or high-risk HPV infections. Here’s a closer look at how these two screening .Best Screening Test. The primary goal of screening is to prevent cervical cancer by detecting treatable abnormalities and precancerous lesions. Early detection of invasive cervical cancer is a.
An HPV test can be done either by itself (primary HPV testing) or at the same time as the Pap test (co-testing). If a Pap test is done by itself and the result is positive (abnormal), the same sample can be used to test for HPV. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Test: Results & Interpretation. Home / Health Library / Diagnostics & Testing / HPV Test. HPV tests detect the strains of human papillomavirus that . The HPV test looks for evidence of the virus in samples from the body. This test may be done at the same time or after another screening test called a Pap test or Pap smear. .
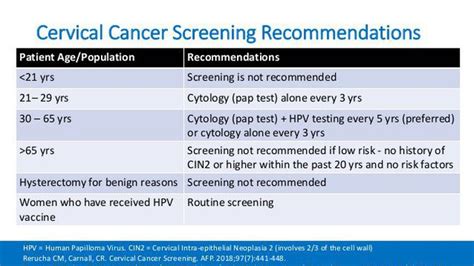
Updated cervical cancer screening guidelines
The HPV test looks for the virus (human papillomavirus) that can cause cell changes on the cervix. The Pap test (or Pap smear) looks for precancers, cell changes on the .Testing for human papillomavirus (HPV) HPV testing is part of cervical screening. There's no blood test for HPV. During cervical screening, a small sample of cells is taken from the cervix and tested for HPV. Screening is offered to all women and people with a cervix aged 25 to 64. It helps protect them against cervical cancer.Currently, HPV tests can only detect HPV if you have a cervix. So, they’re only for people assigned female at birth (AFAB) with an intact cervix. There isn’t an HPV test for people assigned male at birth (AMAB). When is an HPV test performed? You may need an HPV test if: You’re a person with a cervix between ages 30 to 65. The American . The HR-HPV E6/E7 mRNA in the tissues of patients with CINs was detected using RNAscope chromogenic in situ hybridization (RISH). Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was performed to evaluate the expression of .
Diagnostic testing, such as an HPV DNA test, can help determine whether you have a high or low risk HPV strain. Pap smears involve taking some cells from your cervix and examining them. A persistent HPV infection, defined as more than one HPV-positive test on two separate consecutive occasions, is a predictor of progression to cancer. 5 Few long-term studies of high-risk HPV .
An HPV test finds high-risk types of HPV on your cervix that can possibly cause cancer. A Pap test, sometimes called a Pap smear, finds abnormal cell changes on your cervix (but it doesn't directly test for cancer or HPV). Testing is important because it finds early warning signs before they cause problems, so you can get treatment to stay healthy.
HPV vaccination could prevent more than 90% of cancers caused by HPV from ever developing. This is an estimated 33,700 cases in the United States every year. Cervical cancer and pre-cancers. Cervical cancer is the only type of cancer caused by HPV with a recommended screening test for detection at an early stage. The HPV test is most often used in 2 situations: The ACS recommends the primary HPV test* as the preferred test for cervical cancer screening for people 25-65 years of age. (*A primary HPV test is an HPV test that is done by itself for screening. The US Food and Drug Administration has approved certain tests to be primary HPV tests.)Primary HPV testing is an effective screening modality for cervical cancer in average-risk individuals (eTable A), can decrease the total number of screenings a patient needs, and can decrease .
Here’s a closer look at how these two screening methods work. How HPV tests work. The leading cause of cervical cancer is HPV. High-risk strains of HPV cause nearly 70% of cervical cancer cases [3]. With HPV testing, these high-risk strains can be detected early on. HPV tests accomplish this by checking whether genetic material unique to HPV . Introduction On 1 January 2020 the screening programme for the prevention of cervical cancer in women from the age of 35 years of the Statutory Health Insurance (GKV) in Germany changed from an annual cytology examination to cytological and HPV co-testing carried out every three years. A large standard diagnostics laboratory has been using liquid-based .
HPV 16, HPV 18, HPV 31, HPV 33, and HPV 42 are examples of high-risk HPV types that can cause cancer. These HPV types can sometimes avoid the body's immune system, so the body can't get rid of the HPV. The infection can linger over time, causing damage to normal cells that can turn them into abnormal cells, which might later become cancer.Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the Papillomaviridae family. [5] Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. [1] In some cases, an HPV infection persists and results in either warts or precancerous lesions. [2] These lesions, depending on the site affected, increase the .
Updated Guidelines for Management of Cervical Cancer
Cervical lesion grading is critical for effective patient management. A three-tier classification (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia [CIN] grade 1, 2 or 3) based on H&E slide review is widely used. However, for reasons of considerable inter-observer variation in CIN grade assignment and for want of a biomarker validating a three-fold stratification, CAP-ASCCP . Introduction: Since 1 January 2020, diagnostic confirmation of abnormalities detected in the context of cytology/HPV co-testing in cervical cancer screening under the statutory health insurance scheme in women aged 35 and over has been performed according to predefined algorithms. A colposcopy is indicated even in the case of borderline/low-grade . HPV tests are not recommended to screen men, adolescents, or women under the age of 30 years. Most people with HPV do not know they have the infection. They never develop symptoms or health problems from it. Some people find out they have HPV when they get genital warts. Women may find out they have HPV when they get an abnormal Pap test result .You may have some light vaginal bleeding for 1 to 2 days after an HPV test. What the results mean . An HPV test will come back as either negative or positive. A negative HPV test result means that you don't have a high-risk type of HPV that is linked to precancerous changes in the cervix or cervical cancer. A positive HPV test result .
It tests for the kinds of HPV that may lead to cervical cancer. The FDA approved the HPV test to be used for women over 30 years old. It may find HPV even before there are changes to the cervix.Two doses of HPV vaccine are recommended for most persons starting the series before their 15 th birthday. . All vaccines used in the United States, including HPV vaccines, go through extensive safety testing before the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) licenses them. During clinical trials before the licensure, the 9-valent HPV vaccine . HPV increases the chances of a cervical cancer diagnosis. When watching for cervical cancer signs, your HPV status is another factor. The human papillomavirus (HPV) causes several types of cancer in both men and women — including cervical cancer. A second positive HPV test is how Sylvia Zaro found out she had cervical cancer in 2016, at age 46.

Pap test results show whether cervical cells are normal or abnormal. A Pap test may also come back as unsatisfactory. Normal Pap test results: No abnormal cervical cells were found. A normal test result may also be called a negative test result or negative for intraepithelial lesion (area of abnormal growth) or malignancy.. Unsatisfactory Pap test results: The lab . The results of your Pap and HPV test are used to determine if you need additional testing. Positive HPV test, normal pap. If you test positive for HPV and your Pap test is normal, your doctor will most likely recommend repeating the Pap and HPV screening exams in one year. If your second HPV test comes back negative, continue regular Pap and .Learning that you’ll need follow-up testing because you’ve had abnormal test results is scary. Colposcopy is a simple, relatively painless procedure that can give you peace of mind from worry. Colposcopy can help your healthcare provider identify any cancer or precancerous cells early so that you get the treatment you need.The most common high-risk strains found in cancer tissues are HPV 16 and HPV 18. These and other high-risk strains are included when we do HPV testing. A lot of my patients are confused and afraid when they test positive for high-risk strains. As an ob-gyn, here is what I share with them. Having HPV does not mean that you have or will develop .
Theel ES. The past, present, and (possible) future of serologic testing for Lyme disease. J Clin Micro. 2016;54(5):1191-1196. Branda J, Linksy K, Kim Y, et al. Two-tiered antibody testing for Lyme disease with use of 2 enzyme immunoassays, a whole-cell sonicate enzyme immunoassay followed by a VlsE C6 peptide enzyme immunoassay. Ages 30-65: Get an HPV test every 5 years; or an HPV/Pap cotest every 5 years; or a Pap test every 3 years. Over age 65: Ask your doctor if you still need screenings.
Regular screenings play a vital role in helping women prevent cervical cancer, which used to be one of the most common causes of death for women in the United States.. However, many women may wonder which tests they need and how often to get them. The guidelines were recently updated, with important new recommendations about Pap smears, .
Scuff resistance tester Instruments
Scuff resistance tester Machines
UniTV [Código 16 dígitos] (30D) quantidade. Adicionar ao carrinho Comprar . Compartilhar: Descrição. Você também pode gostar desses . Quick view. BlueTV (30D) R$ 19,90 Em até 1 x de R$ 19,90 sem juros R$ 18,51 no pix. Comprar. Canais de TV Compatível com Android Não é compatível com SmarTV ⚠️ Validade de 30 dias(após uso)
two tear testing for hpv|HPV Test vs. Pap Smear: What's the Difference?